Similar to variables, Utility Methods in vREST provides a way to dynamically change the test case properties at run time. Utility Methods
- provide dynamic values to test cases.
- are also available to Response Validators as a third argument.
Utility methods in vREST, can be accessed by using the format {{method_name(argument1, argument2, ...)}}.
By Default, 4 utility methods are available in vREST.
- compareJSON :
This method compares two JSON objects and returns boolean according to whether the two JSON objects are identical to each other or not. This method is used in Response Validator "Default Validator" and non-editable.
- validateJSONSchema
This method validates whether the JSON object matches with the provided JSON schema. This method is also used in Response Validator and non-editable.
- getRandom
This method returns a random number of length 7 if no arguments are passed or returns a random integer between min (included) and max (excluded). This method is also non-editable.
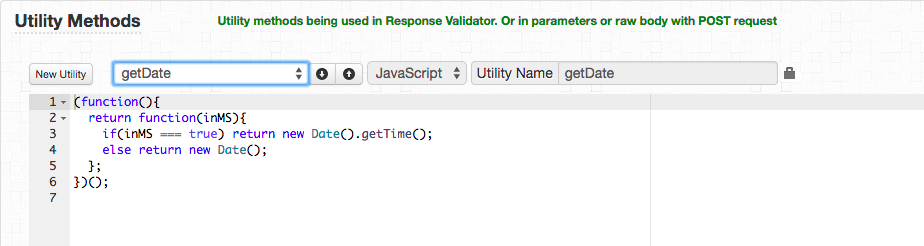
- getDate
This method returns a date timestamp string if no arguments are passed or returns the number of milliseconds between midnight of January 1, 1970 and the current date if true is passed as an argument. This method is also non-editable.
Apart from built-in utility methods, an user can create custom utility methods by clicking on "New Utility" button in "Utility Methods" section. Similar to variables, utility methods can be used in:
- Request URL
- Request Parameter value
- Request Header value
- Request Raw Body
- Response Expected Body
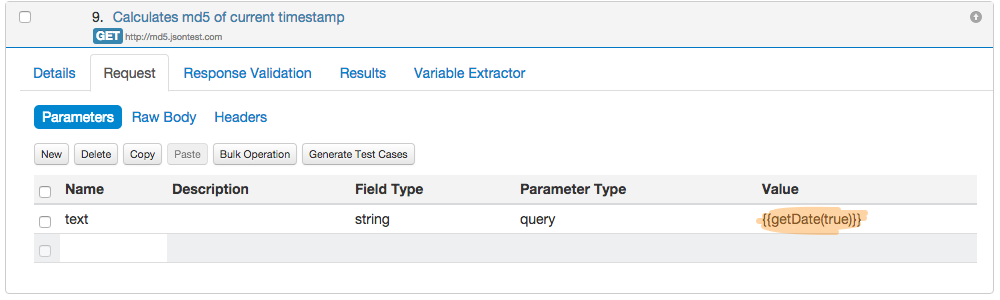
Lets take an example, how utility methods are useful in testing. Suppose we have an API which accepts a parameter having current timestamp. How you can provide values to such test cases? Utility Methods are a solution:
- First define a utility method in the "Utility Methods" section or use any built-in utility method like so
- Then use this utility method in your test case like this